Size of the Genes:
The size the RNA or the protein it produces can roughly estimate size of the gene. In general most of the rRNA, and tRNA, sn/sc RNA and mRNA genes are smaller than the size of precursors. This holds good for both prokaryotes as well as eukaryote. The size, however, vary considerably from system to system and from one gene to another. Interestingly, the size of a specific gene of one species is more or less same in another species, with certain exceptions. But comparisons of certain gene from prokaryote with that of a eukaryote for the same gene show considerable variation, but the overall coding sequences show certain degree of similarity, again with certain exception and generalization between prokaryotes and eukaryotes cannot be made. Actual size of the gene should take into the account of spacer region within the gene or non-coding regions in the gene; however the size should include promoter and its related elements and terminal sequence elements. Ultimately the size of the mRNA in prokaryotes is more or less equals to the size of the protein, so the size of the gene. But the functional mRNA or the protein produced does not give the accurate size of the gene for in eukaryotes the size of the gene includes regulatory regions, introns and other non-coding regions.
|
Name of the Gene, (only Few) |
Size of the gene (BP) |
Size of Hn RNA |
|
|
b Globin |
1500 |
1382 |
|
|
Human insulin |
1700 |
|
|
|
Rat insulin type II |
1500 |
|
|
|
Protein kinase |
11 000 |
|
|
|
Ovalbumin |
8 000 |
7700 |
|
|
Serum albumin |
25 000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Catalase |
34 000 |
|
|
|
LDL receptor |
45 000 |
|
|
Apolipoprotein |
> 500 bp isoforms |
|
|
|
Actin |
1500 |
|
|
|
Clotting factor VIII |
186 000 |
|
|
|
Thyroglobulin |
300 000 |
|
|
|
Dystrophin |
2.2-2.4 x10^6 |
79exons |
|
|
Ovomucoid |
~5.5-5.6kb |
|
|
|
Alcohol dehydrogenase |
|
|
|
|
Di hydrofolate reductase |
31 000 |
|
|
|
DMD, membrane protein |
200-250kbp |
|
|
|
Pyruvate kinase |
12,142 bp |
|
|
|
Rat fatty acid synthase |
~18kbp |
|
|
|
a Tropomycin (7 types) |
~29,284 bases |
|
|
|
Chick collagen 1a2 |
40 000 |
|
|
Fibronectin |
75 000 |
|
|
|
Titin |
38,138x3+200+ , 304,814bp 364exons |
3816.30kDa a.a 4200kDa 244 domains |
|
|
Ovalbumin |
7.8 kb |
|
|
|
CNTNAP2 |
2.3mb |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
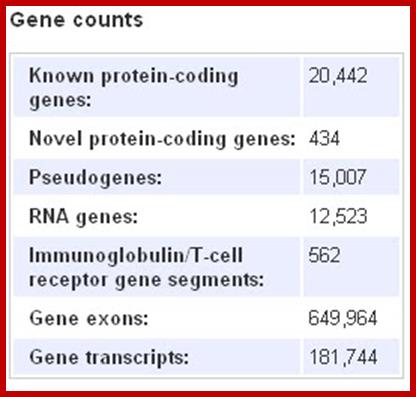
Human Gene count:
Data from ensemble; it indicates human genome contains 33399 genes?
Lawerence A.moran-sandwalk
Number and Size of rRNA and tRNA Genes:
|
System |
5s RNA |
|
tRNA |
|
[16s/23/5s |
18s/28s/5.8s] |
|
|
Size in BP |
Number Per genome |
Size in BP |
Number per genome |
Size in BP |
Number Per genome |
|
E.coli |
|
|
~5-7kbp Operon |
60 |
5.8 to 5.9kbp |
7 |
|
Yeast |
300kbp |
140 |
Clusters 150-200bp |
250-400 |
5.95KBP |
140 |
|
D.melanogaster |
300bp
|
165 |
Clusters 150-200bp |
850 |
11.2 14.2kbp |
250 |
|
X.laevis |
300bp |
24000 |
Clusters 150-200bp |
1150 |
10.5 to13.5kbp |
450-600 |
|
Mus musculus |
300bp |
200 |
|
|
12.5kbp |
200 |
|
Homo sapien |
300bp |
1300-2000 |
150-200bp |
1300-2000 |
13.7kbp |
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Each of the genes as units has specific sizes, which is measured in terms of base pairs.
The size varies from as small as 150 bp to 2,500,000 bp or longer. The size just indicates the whole size, but it need not be represented in its RNA product base by base or its protein.
Comparing the exact size of the gene and the size of its final RNA, the size of the Gene is greater than its final RNA; sometimes it is several times the size of the final RNA. The start and the end, with the exception of overlapping genes, delimit each gene.
Average size of a prokaryotic gene is ~1000 ntds and that of a eukaryotic gene is ~1500 to ~2000 ntds. At both ends of a gene there are noncoding sequences, actually the coding region lies in between the start codon and a terminator codon.
In prokaryotes the mRNA transcript consists of individual cistrons one to many, each cistron code for a specific polypeptide chain. In polycistronic mRNAs spacer is found which helps in ribosomes dissociating from the mRNA and reassociating to initiate the chain. But eukaryotic coding sequences are invariably interrupted with noncoding sequences called Introns; sometimes the total size of the intervening regions can be many times longer than the actual coding size.